Google’s newest flagship I/O convention noticed the corporate double down on its Search Generative Expertise (SGE) – which is able to embed generative AI into Google Search.
SGE, which goals to deliver AI-generated solutions to over a billion customers by the tip of 2024, depends on Gemini, Google’s household of enormous language fashions (LLMs), to generate human-like responses to go looking queries.
As an alternative of a standard Google search, which primarily shows hyperlinks, you’ll be introduced with an AI-generated abstract of outcomes, basically summarising the reply to your question.
This “AI Overview” has been criticized for offering nonsense data, and Google is quick engaged on options earlier than it begins mass rollout.
However other than recommending including glue on pizza and saying pythons are mammals, there’s one other bugbear with Google’s new AI-driven search technique: its environmental footprint.
Whereas conventional serps merely retrieve current data from the web, generative AI methods like SGE should create solely new content material for every question. This course of requires vastly extra computational energy and power than standard search strategies.
Billions of Google searches are performed every day, between 3 and 10 billion, in response to most estimates. The impacts of making use of AI to even a small proportion may very well be unbelievable.
Sasha Luccioni, a researcher on the AI firm Hugging Face who research the environmental affect of those applied sciences, just lately mentioned the sharp enhance in power consumption SGE would possibly set off.
Luccioni and her workforce estimate that producing search data with AI may require 30 instances as a lot power as a traditional search.
“It simply is smart, proper? Whereas an earthly search question finds current knowledge from the Web, purposes like AI Overviews should create solely new data,” she advised Scientific American.
In 2023, Luccioni and her colleagues discovered that coaching the LLM BLOOM emitted greenhouse gases equal to 19 kilograms of CO2 per day of use, or the quantity generated by driving 49 miles in a mean gas-powered automotive. In addition they discovered that producing simply two photos utilizing AI can eat as a lot power as totally charging a mean smartphone.
Earlier research have additionally assessed the CO2 emissions associated to AI mannequin coaching, which could exceed the emissions of a whole lot of economic flights or the common automotive throughout its lifetime.
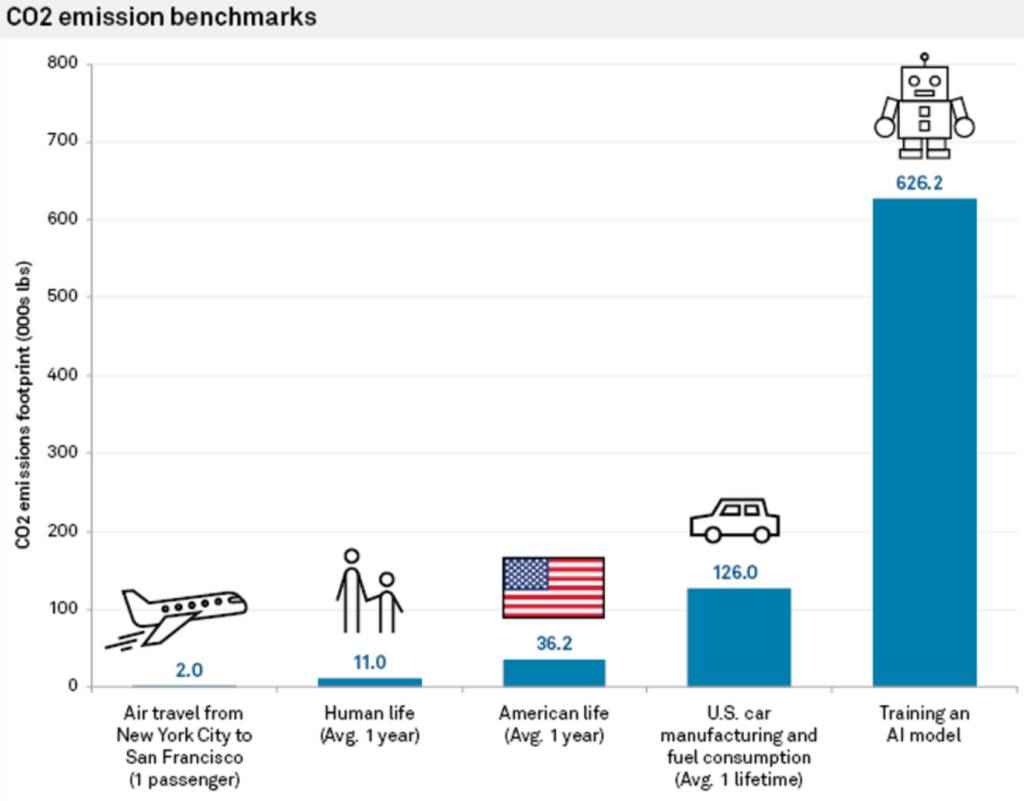
In an interview with Reuters final yr, John Hennessy, chair of Google’s guardian firm, Alphabet, himself admitted to the elevated prices related to AI-powered search.
“An change with a big language mannequin may value ten instances greater than a standard search,” he acknowledged, though he predicted prices to lower because the fashions are fine-tuned.
AI search’s pressure on infrastructure and sources
Knowledge facilities housing AI servers are projected to double their power consumption by 2026, probably utilizing as a lot energy as a small nation.
With chip producers like NVIDIA rolling out greater, extra highly effective chips, it may quickly take the equal of a number of nuclear energy stations to run large-scale AI workloads.
When AI firms reply to questions on how this may be sustained, they usually quote renewables’ elevated effectivity and capability and improved energy effectivity of AI {hardware}.
Nonetheless, the transition to renewable power sources for knowledge facilities is proving to be gradual and sophisticated.
As Shaolei Ren, a pc engineer on the College of California, Riverside, who research sustainable AI, defined, “There’s a provide and demand mismatch for renewable power. The intermittent nature of renewable power manufacturing typically fails to match the fixed, secure energy required by knowledge facilities.”
On account of this mismatch, fossil gasoline crops are being saved on-line longer than deliberate in areas with excessive concentrations of tech infrastructure.
Improvements in energy-efficient AI {hardware} are positively impacting AI’s power footprint, with firms like NVIDIA and Delta making large strides in decreasing their {hardware}’s power footprint.
Rama Ramakrishnan, an MIT Sloan College of Administration professor, defined that whereas the variety of searches going via LLMs is prone to enhance, the price per question appears to lower as firms work to make {hardware} and software program extra environment friendly.
However will that be sufficient to offset growing power calls for? “It’s tough to foretell,” Ramakrishnan says. “My guess is that it’s most likely going to go up, however it’s most likely not going to go up dramatically.”
Because the AI race heats up, mitigating environmental impacts has change into crucial. Necessity is the mom of invention; the stress is on tech firms to create options to maintain AI’s momentum rolling.
SGE may pressure water provides, too
We are able to additionally speculate in regards to the water calls for created by SGE, which is able to doubtless mirror will increase in knowledge middle water consumption attributed to the generative AI trade.
Based on latest Microsoft environmental studies, water consumption has rocketed by as much as 50% in some areas, with the Las Vegas knowledge middle water consumption doubling. Google’s studies additionally registered a 20% enhance in knowledge middle water expenditure in 2023 in comparison with 2022.
Shaolei Ren, a researcher on the College of California, Riverside, attributes the vast majority of this development to AI, stating, “It’s honest to say the vast majority of the expansion is because of AI, together with Microsoft’s heavy funding in generative AI and partnership with OpenAI.”
Ren estimated that every interplay with ChatGPT, consisting of 5 to 50 prompts, consumes a staggering 500ml of water.
In a paper revealed in 2023, Ren’s workforce wrote, “The worldwide AI demand could also be accountable for 4.2 – 6.6 billion cubic meters of water withdrawal in 2027, which is greater than the overall annual water withdrawal of 4 – 6 Denmark or half of the UK.”
Utilizing Ren’s analysis, we will create some serviette calculations for the way Google’s SGE would possibly issue into these predictions.
Let’s say Google processes a mean of 8.5 billion every day searches worldwide. Assuming that even a fraction of those searches, say 10%, make the most of SGE and generate AI-powered responses with a mean of fifty phrases per response, the water consumption may very well be phenomenal.
Utilizing Ren’s estimate of 500 milliliters of water per 5 to 50 prompts, we will roughly calculate that 850 million SGE-powered searches (10% of Google’s every day searches) would eat roughly 85 billion milliliters or 85 million liters of water every day.
That is equal to the every day water consumption of a metropolis with a inhabitants of over 500,000 folks day by day.
In actuality, precise water consumption could range relying on elements such because the effectivity of Google’s knowledge facilities and the particular implementation and scale of SGE.
However, it’s very affordable to take a position that SGE and different types of AI search will additional ramp up AI’s useful resource utilization.
How the trade reacts will decide whether or not international AI experiences like SGE could be sustainable at an enormous scale.

